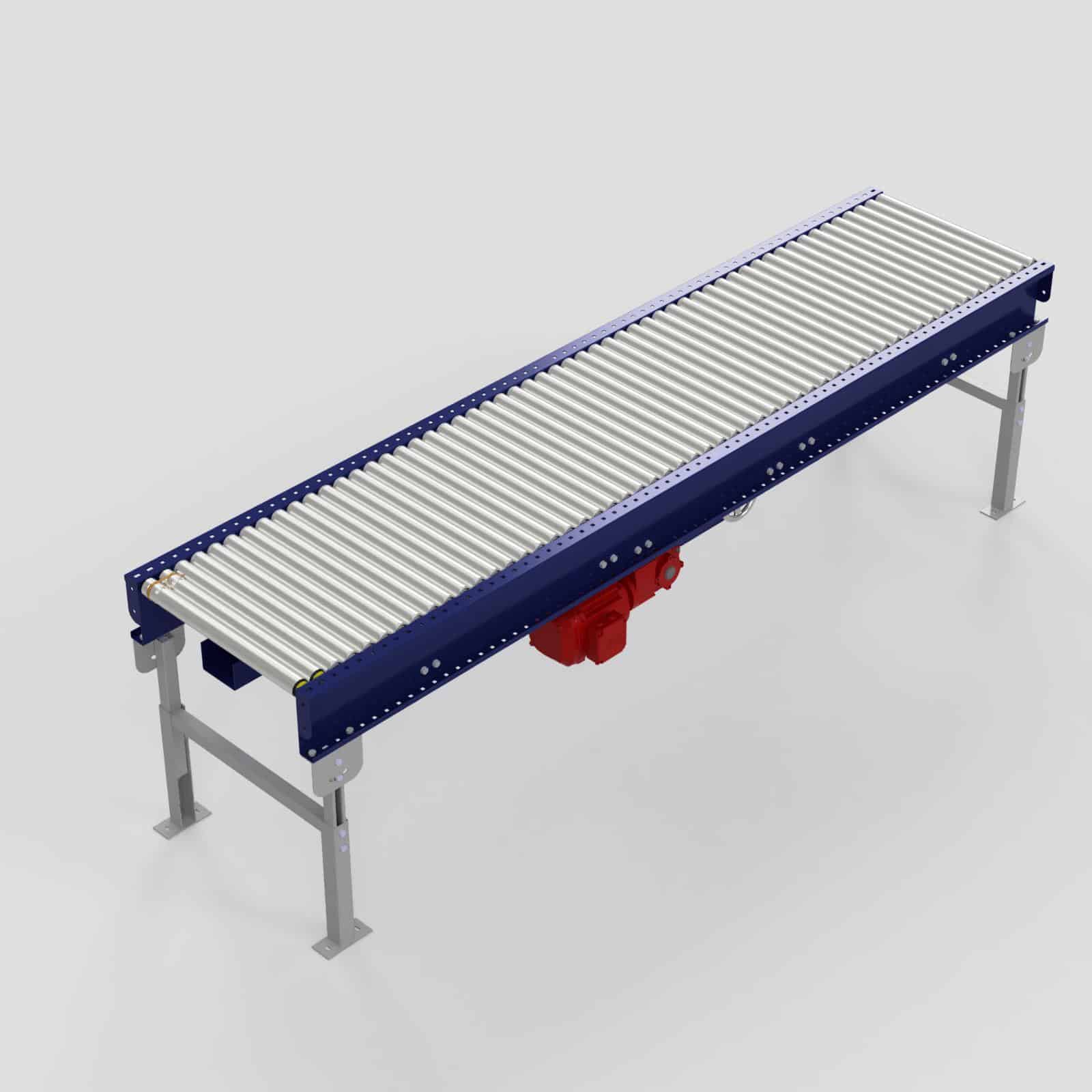
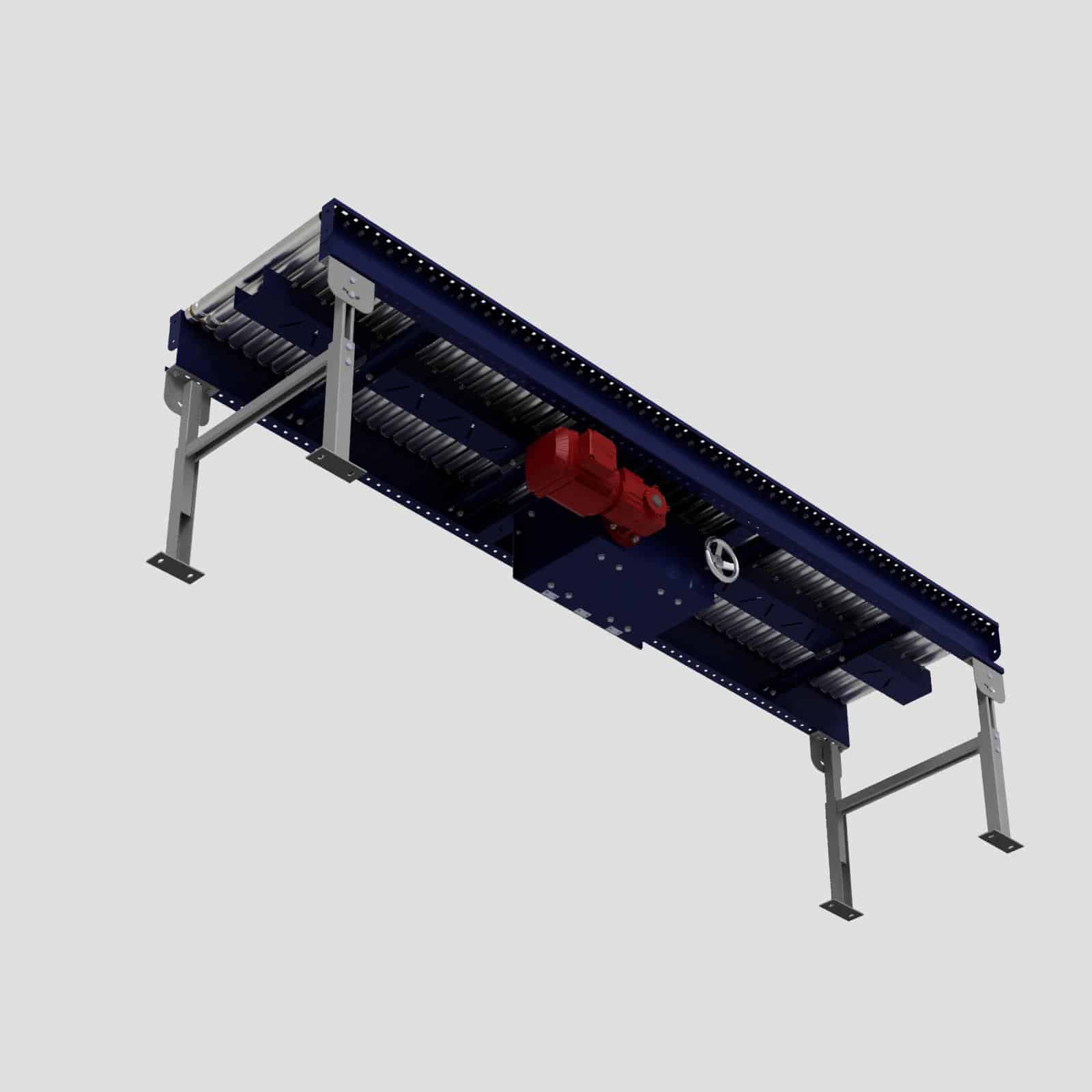
A powered conveyor is a type of material handling system that uses an external power source, such as an electric motor, to move objects along a fixed path or track. These conveyors actively propel the materials being transported, instead of relying completely on gravity.
Contents
- Introduction
- Powered Conveyors key applications and use cases
- Powered conveyors advantages
- Powered conveyors disadvantages
- Ask us about Powered Conveyors
1. Introduction
Powered conveyors uses a motor attached to a drive mechanism (such as belts, rollers, or chains), and a supporting structure or frame. The motor provides the necessary power to drive the conveyor belt, rollers, or other components to move materials along the conveyor path. Conveyors can be designed to operate horizontally, vertically, or at various angles, allowing for more options in routing and material flow compared to gravity conveyors.
Powered conveyors are commonly used in industrial settings, such as manufacturing plants, warehouses, and distribution centers, where a continuous and controlled flow of materials is required. They can handle a wider range of materials, including heavy or bulky items, and can be configured with various features like accumulation zones, diverters, and sortation capabilities to meet specific material handling needs.
2. Powered Conveyors key applications and use cases
- Manufacturing and assembly lines: Powered conveyors are essential in modern manufacturing facilities, allowing for the continuous movement of components, and finished products along the production line.
- Warehousing and distribution: In warehouses and distribution centers, powered conveyors are used to transport goods, packages, and pallets between various areas, such as receiving docks, storage locations, and shipping areas.
- Baggage handling systems: Airports and other transportation hubs rely on powered conveyors to move luggage and cargo through the handling process.
- Food and beverage processing: Powered conveyors are commonly used in food processing plants and bottling facilities to move raw materials, finished products, and packaging materials through various stages of production.
- Sorting and order fulfillment: Powered conveyors with integrated sortation capabilities can automatically divert and route items to different destinations, streamlining order picking and fulfillment processes.
- Automotive industry: Powered conveyors play a crucial role in automotive manufacturing plants, transporting vehicle components, sub-assemblies, and finished vehicles through the various stages of production.
The ability to handle heavy loads, provide continuous and controlled material flow, and integrate with other automated systems makes powered conveyors an indispensable part of many modern industrial and logistics operations.
3. Powered conveyors advantages
1. Continuous material flow: Powered conveyors can provide a consistent and uninterrupted flow of materials, allowing for higher throughput and productivity compared to manual or gravity-based systems.
2. Versatility: Powered conveyors can be configured to operate horizontally, vertically, or at various angles, making them suitable for a wide range of material handling applications and facility layouts.
3. Automation capabilities: Powered conveyors can be integrated with other automated systems, such as sorting machines, diverters, and control systems, enabling advanced material handling and distribution processes.
4. Increased load capacity: Powered conveyors can handle heavier and bulkier items than gravity conveyors, making them suitable for transporting a wider range of materials.
4. Powered conveyors disadvantages
1. Higher initial and operating costs: Powered conveyors require an external power source, such as electricity, and involve more complex mechanical components, resulting in higher upfront and ongoing maintenance costs compared to gravity conveyors.
2. Potential safety hazards: Moving parts and the continuous operation of powered conveyors can pose potential safety risks to workers if proper safety measures and guarding are not implemented.
3. Energy consumption: Powered conveyors consume energy (typically electricity) to operate, which can result in higher operating costs and a larger environmental footprint compared to gravity-based systems.
4. Complexity: Powered conveyors often involve more complex systems, requiring specialized installation, maintenance, and skilled personnel to operate and troubleshoot effectively.
While powered conveyors have higher costs and complexity, their ability to provide continuous material flow, handle heavier loads, and integrate with automated systems makes them a crucial component in many industrial and logistics operations where efficiency, productivity, and throughput are critical factors.
5. Ask us about Powered Conveyors:
If you would like advise on getting the right gravity conveyor, or need something more bespoke get in touch, or give us a call on 0161 793 0707.